RIYADH: Artificial intelligence in healthcare is revolutionizing medical diagnostics, from streamlining patient care to enhancing the speed and accuracy of disease detection.
Saudi Arabia is at the forefront of this revolution with the development of an innovative AI model called MiniGPT-Med, which promises to reshape how medical professionals approach diagnostics.
With the ability to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns that might be missed by the human eye, AI is fast becoming an indispensable healthcare tool.
Whether detecting early signs of diseases, interpreting medical scans or helping plan treatment, AI’s role in medicine is expanding rapidly, reducing costs and improving patient outcomes.
Enter MiniGPT-Med, a cutting-edge, vision-interfaced AI model developed in Saudi Arabia by the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in collaboration with the Saudi Data and Artificial Intelligence Authority.
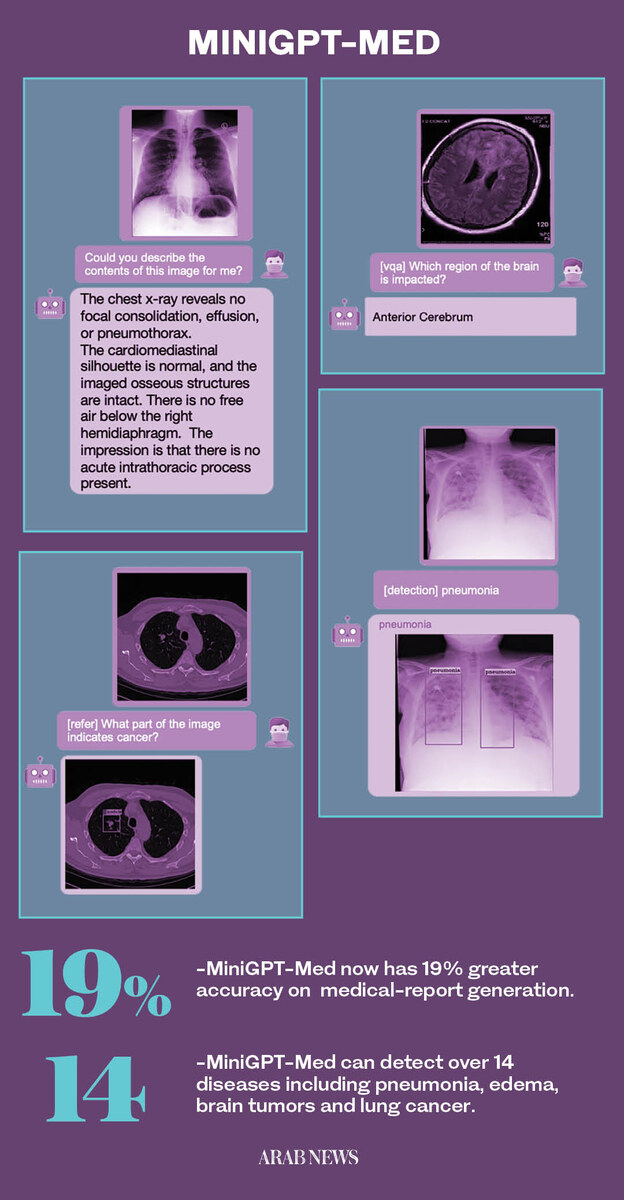
Launched in July, this advanced tool is designed to enhance the accuracy of medical diagnostics by integrating image analysis with textual clinical data, significantly improving the detection of conditions such as pneumonia, edema, brain tumors and lung cancer.
“MiniGPT-Med aids doctors by improving diagnostic accuracy through integrated processing of both image and textual clinical data,” Mohamed Elhoseiny, assistant professor of computer science at the Visual Computing Center at KAUST, told Arab News.
“It can be thought of as giving a large language model medical eyesight by carefully integrating vision into the language model and preparing the necessary data to learn these skills, including the localization of issues in medical images.”
MiniGPT-Med builds on the existing architecture of large language models — or LLMs — like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, which have already demonstrated exceptional medical knowledge.
Opinion
This section contains relevant reference points, placed in (Opinion field)
One of the key features that sets MiniGPT-Med apart from other AI models is its ability to localize abnormalities within medical images.
Doctors interact with it using simple, predefined queries such as “Could you describe the contents of this image for me?” or “Where is the abnormality?”
The AI then provides immediate, accurate results, such as identifying pneumonia in a chest X-ray or pinpointing the exact region of a brain tumor in an MRI scan.

In initial trials, it has already surpassed the accuracy of previous models by as much as 19 percent.
Trained on diverse medical datasets, MiniGPT-Med leverages millions of cases to back up its diagnoses, drawing reasoned conclusions by comparing images to similar cases in its database.
DID YOUKNOW?
• MiniGPT-Med enhances diagnostic accuracy by integrating image analysis with clinical data.
The AI model identifies diseases such as pneumonia, edema, brain tumors, and lung cancer.
• It localizes abnormalities in medical images, helping doctors to make precise diagnoses.
• Developed by KAUST and SDAIA, it is part of Saudi Arabia’s drive to lead in AI healthcare.
The model sources its information from five comprehensive medical datasets, including MIMIC-CXR (chest X-ray images and reports), NLST (low-dose CT scans for lung cancer detection), SLAKE (radiology images), RSNA (pneumonia detection), and RadVQA (radiology images).
Despite its accuracy, Elhoseiny is keen to emphasize that MiniGPT-Med is designed to complement, not replace, healthcare professionals.
“The new diagnostics method introduced by models like MiniGPT-Med aims to assist, not replace, physicians and radiologists, enabling them to do more with less,” he said.

Instead, by enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, the AI tool is intended to help doctors deliver better care, especially in under-resourced areas.
Looking to the future, the development team at KAUST and SDAIA plans to incorporate more diverse datasets, improve the model’s understanding of complex medical terminology, and enhance its reliability.
Extensive clinical validation studies are also planned to ensure that MiniGPT-Med is safe and effective in real world healthcare environments.
The collaboration between KAUST and SDAIA represents a significant step forward in the application of AI in healthcare.

Elhoseiny says the partnership is aligned with the broader goals of the new GenAI Center of Excellence at KAUST, where further innovations in AI are expected to emerge.
With technologies like MiniGPT-Med, Saudi Arabia is not only advancing its healthcare capabilities but also positioning itself as a leader in the global AI landscape.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the promise of transforming healthcare practices worldwide, offering hope for more accurate diagnoses and better patient outcomes.


































